
Forget the idea that a single magical piece of software will keep your business network safe. The smartest approach isn’t about one product; it’s about building a layered, strategic framework. We call this defense-in-depth, and the concept is simple: if one security layer gets breached, several others are standing by to protect your most critical data and systems.
Your Blueprint for a Resilient Business Network
A truly secure and reliable network doesn’t happen by accident. I’ve seen too many businesses fall into the trap of buying security tools reactively, usually after a scare. This creates a messy patchwork of solutions that don’t communicate, leaving dangerous gaps an attacker can slip through.
A much better way is to build a cohesive strategy from the ground up. It all starts with a simple question: what are you trying to protect, and why is it important? From there, you can move beyond just a firewall and basic antivirus. Real network resilience comes from several core pillars working together seamlessly. You need to meticulously control who gets in, protect the information flowing across your network, and have a rock-solid plan to get back on your feet when—not if—something goes wrong.
Understanding the Core Security Workflow
To build a strategy that actually works, you have to follow a logical path from initial assessment to day-to-day management. This isn’t a one-and-done project; it’s a continuous cycle.
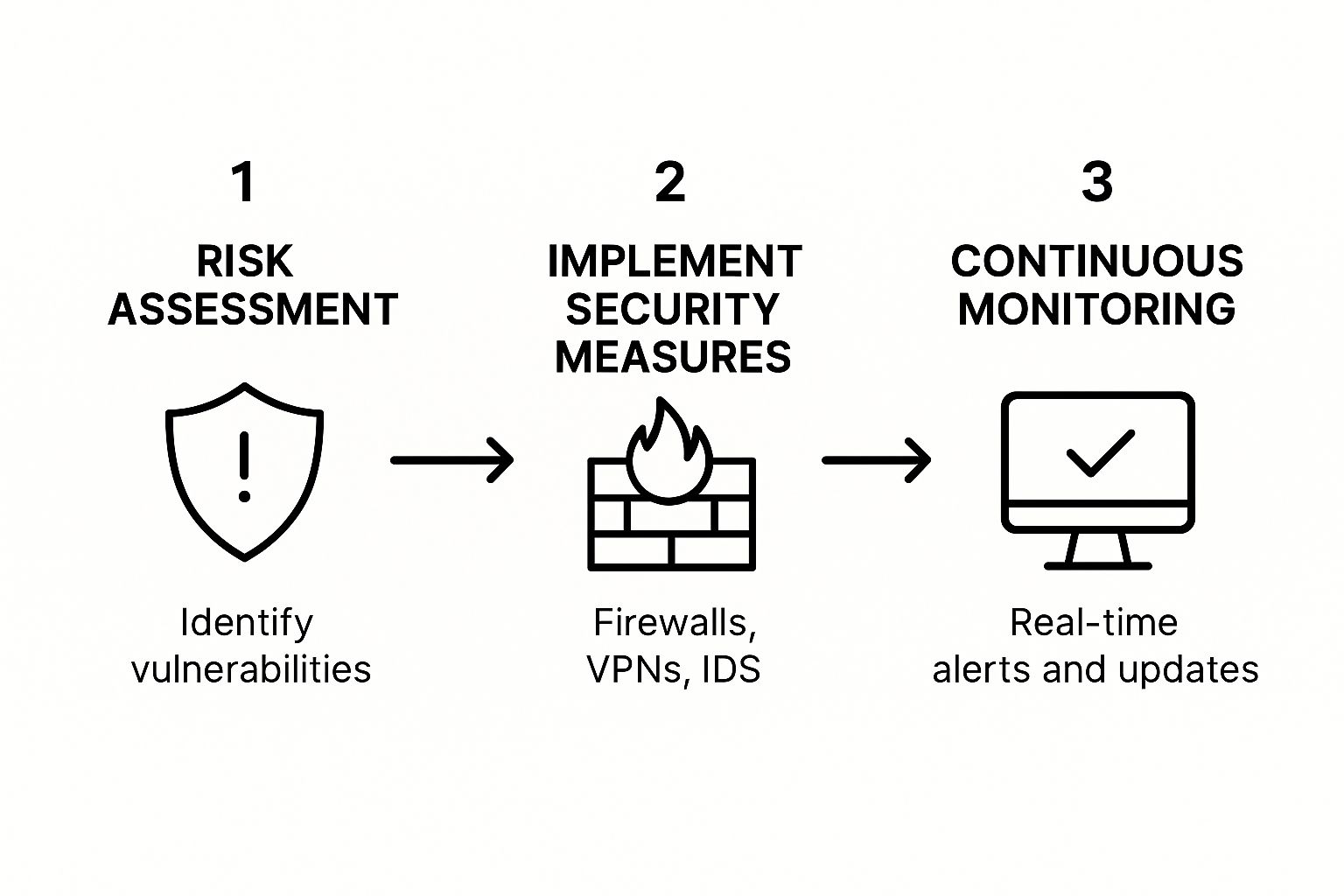
The image above breaks it down into three foundational stages: Assess, Implement, and Manage. This flow shows that strong security is an ongoing commitment involving risk identification, deploying the right protections, and keeping a watchful eye on everything.
This integrated approach is what separates a tough, resilient network from an easy target. It’s all about creating a security posture that is both strong and flexible enough to adapt to new threats. When you commit to this lifecycle, your network stops being a potential liability and becomes a powerful asset that supports your business’s growth and stability.
The ultimate goal is to make your network an unattractive and difficult target for attackers while ensuring it remains highly available for legitimate business use. This balance is the key to both security and reliability.
To put it all together, here’s a quick overview of the essential strategies we’ll be covering. Think of these as the fundamental building blocks for your network security and reliability plan.
Core Pillars of Network Security and Reliability
| Strategy | Objective | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities | Conduct a thorough audit of all network assets and potential threats. |
| Perimeter Defense | Secure the network’s entry and exit points | Implement and configure firewalls, VPNs, and email security. |
| Segmentation | Contain threats and limit lateral movement | Isolate critical systems from the general network to reduce attack surface. |
| Patch Management | Close known security holes in software | Establish a consistent process for testing and deploying updates. |
| Monitoring & Logging | Detect and respond to suspicious activity | Use SIEM and other tools to gain visibility into network traffic. |
| Backups & Redundancy | Ensure business continuity after an incident | Create regular, verified backups and build failover systems. |
| Managed Services | Leverage expert support for complex tasks | Partner with an MSP for specialized security and network management. |
Each of these pillars plays a crucial role. By addressing them systematically, you create a comprehensive defense that is far more effective than any single solution could ever be.
Building Your First Line of Defense
A secure network starts at its perimeter—that digital border where your private business data meets the public internet. This isn’t about throwing up a simple wall; it’s about creating a smart, active barrier that inspects everything coming in and going out. Honestly, this is the most critical first step to keeping your business network secure and reliable.

The days of a basic firewall being “good enough” are long gone. Your frontline defense today needs to be a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) working hand-in-hand with an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS). Think of it like a security guard who doesn’t just check IDs at the door. This guard understands context, inspects every package, and spots suspicious behavior before trouble starts.
For example, you can set rules to automatically block all traffic from countries where you don’t do business. An IPS can spot a brute-force attack on your remote access portal and shut it down instantly, long before a hacker gets in. These are the kinds of proactive measures that define modern, robust https://omxsolutions.com/network-solutions/.
The Power of Divide and Conquer
Once your perimeter is solid, it’s time to apply a “divide and conquer” strategy inside your network. We call this network segmentation, and it’s a total game-changer for containing threats. Instead of one big, flat network where every device can talk to every other device, you create smaller, isolated zones.
Imagine your network is a building. A flat network is like a giant, open-plan office—if a fire starts in one corner, it can race through the entire space in minutes. Segmentation, on the other hand, is like building fire-rated walls between departments, creating separate, secure rooms.
- Finance Department: This zone holds your sensitive accounting systems and financial data. Only authorized finance team members can get in.
- HR Department: Employee records and other confidential info live here, completely walled off from other business units.
- Guest Wi-Fi: This is a totally separate island. It gives visitors internet access without letting them anywhere near your internal company resources, protecting you from their potentially compromised devices.
This structure cripples an attacker’s ability to move around. If the guest Wi-Fi gets compromised, the threat is stuck there. The attacker can’t just hop over and start siphoning data from your finance servers.
By creating these digital bulkheads, you shrink your attack surface significantly. A breach in one segment doesn’t have to become a company-wide disaster; it becomes a manageable, contained incident.
Investing in the Right Foundation
Building this kind of layered defense means making a smart investment in both hardware and software. Data from the Middle East & Africa (MEA) cybersecurity market really drives this point home. The market generated roughly USD 16.5 billion in revenue, and hardware accounted for nearly 64% of that.
This shows just how critical physical infrastructure—like powerful firewalls and secure routers—is to protecting your network. A reliable network is always built on a solid, well-equipped foundation.
Adopting a Proactive Zero Trust Mindset
For decades, we thought about network security like a medieval fortress. We built a strong wall—a perimeter—and assumed everything inside was safe. That “castle-and-moat” thinking is officially dead. The modern workplace, with its mix of remote staff, cloud apps, and personal devices, has erased the old boundaries.
This is where the Zero Trust model comes in, and it’s built on a beautifully simple premise: never trust, always verify. Instead of giving a free pass to traffic just because it’s already “inside,” every single request to access a resource has to be authenticated and authorized. It’s one of the most effective strategies available today for keeping your business network secure and reliable.
Shifting from Trust to Verification
When you fully embrace Zero Trust, you operate under the assumption that a breach is not a matter of if, but when—or that one might have already happened. It sounds a bit grim, I know, but this mindset forces you to build defenses that are far more resilient. You’re suddenly prepared for external attackers who find a way in and for insider threats, whether they’re malicious or just plain accidental.
So, how does this work in practice? It means a single password is never enough. Every user and every device has to prove its identity, every single time. This usually boils down to a few core practices:
- Universal Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This one is non-negotiable. Every login to every system, whether it’s a cloud service or an internal server, must be backed by a second factor. Think codes from an authenticator app, a fingerprint scan, or a physical hardware key.
- The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Give people access only to the specific data and systems they absolutely need to do their jobs, and nothing more. The marketing coordinator has no business accessing finance department servers, and the accounting team shouldn’t be able to browse the developer’s code repository.
Zero Trust isn’t a single product you can just go out and buy. It’s a strategic shift in your security philosophy. You move from the old idea of “trust, but verify” to “never trust, always verify,” and in doing so, you drastically shrink your attack surface.
Containing Threats with Micro-Segmentation
One of the most powerful tactics in a Zero Trust arsenal is micro-segmentation. Traditional network segmentation might create a big, broad zone for, say, the entire HR department. Micro-segmentation takes this concept down to a granular level, placing tight security controls around individual applications or even specific workloads.
Think of it like putting a critical accounting application inside its own hardened, isolated bubble. Even if a cybercriminal manages to compromise a server sitting right next to it, they can’t move laterally to access that application without going through another gauntlet of strict verification checks. This is absolutely critical for stopping attackers in their tracks.
This approach is more important than ever. The MENA Cyber Summit Annual Report highlighted that many organizations still haven’t implemented Zero Trust architectures, leaving them dangerously exposed by assuming some internal network traffic is safe. In reality, continuous verification for all users and devices is no longer a “nice to have”—it’s a fundamental necessity. You can dive deeper into the full report on MENA cyber security trends to learn more.
Keep a Watchful Eye with Active Monitoring
Once you’ve built a secure network, the job isn’t over. Far from it. Think of it like owning a high-performance car. You wouldn’t just build the engine and then never check the oil or listen for strange noises. It needs constant attention and regular tune-ups to keep running smoothly and safely.

The same daily discipline is what keeps your network secure and reliable over the long haul. Two of the most critical practices here are systematic patch management and continuous monitoring. If you drop the ball on either, you might as well leave the front door unlocked for attackers.
The Never-Ending Discipline of Patch Management
Every single piece of software on your network, from the operating system on a server to the browser on a laptop, can have security flaws. When developers find these weaknesses, they release patches to fix them. Patch management is simply the process of making sure those fixes get applied everywhere, consistently.
It really is a race against time. Bad actors are constantly scanning for unpatched systems because they are the lowest-hanging fruit. A structured approach isn’t just nice to have; it’s essential.
- Test Before You Deploy: Never just push updates out to everyone at once. Always test patches in a controlled, non-critical environment first. The last thing you want is a security patch that accidentally takes down your entire sales platform.
- Prioritize Ruthlessly: Focus on the biggest risks first. Patches for critical vulnerabilities, especially on systems that face the public internet (like your website or VPN), need to be at the top of the list.
Failing to patch is one of the most common—and frankly, most avoidable—ways businesses get breached. It’s the basic, foundational maintenance that locks the door on known threats.
See Everything with SIEM
Patching closes the known security holes, but what about the unknown threats or just plain weird activity? That’s where a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system comes into play. Think of a SIEM as the central security hub for your entire network.
It pulls in and makes sense of log data from all your different devices—firewalls, servers, workstations, you name it. By looking at everything together, it can spot suspicious patterns that would be completely invisible if you were just looking at one device at a time.
Imagine getting an alert because an employee’s account, which is always used from your Dubai office during the day, suddenly tries to access a sensitive database at 3 AM from a server in Eastern Europe. That’s the kind of early warning a good monitoring system gives you.
This real-time visibility means you can jump on a potential threat right away, not find out about a breach weeks or even months after the damage is done. SIEM tools are fundamental because they transform a tidal wave of raw data into intelligence you can actually use, helping you stop threats before they escalate.
Keeping the Lights On with Backups and Redundancy
Let’s be realistic: even with the best defenses, things can go wrong. A server can fail, a construction crew can cut a fiber line, or a nasty piece of ransomware could slip through. When disaster strikes, the difference between a minor hiccup and a business-ending catastrophe is your plan for getting back up and running.
This is where a solid safety net comes in, built on two pillars: data backups and network redundancy. Think of it as insurance for your operations. One protects your data, and the other protects your ability to actually use that data.
The 3-2-1 Rule: Your Data’s Best Friend
When it comes to backups, simply dragging files to an external hard drive doesn’t cut it anymore. The industry-standard approach, and one I’ve seen save countless businesses, is the 3-2-1 rule. It’s a surprisingly simple concept that builds incredible resilience.
Here’s the breakdown:
- Keep three copies of your important data.
- Store those copies on two different types of media.
- Make sure one of those copies is kept off-site.
So, what does that look like in the real world? Your live data sits on your primary server (that’s copy #1). A second copy gets backed up automatically every night to a local Network-Attached Storage (NAS) device (that’s copy #2 on different media). Finally, a third, encrypted copy is sent to a secure cloud service (that’s copy #3, safely off-site). This strategy protects you from a single drive failure just as well as it protects you from a fire or flood at your office.
A backup you haven’t tested is just a guess. Seriously. You have to schedule regular recovery drills to make sure the data is actually usable and you can get it back within an acceptable timeframe.
Eliminating Single Points of Failure with Redundancy
While backups are about recovering your data after an incident, redundancy is about preventing the incident from taking you offline in the first place. Network redundancy is all about having fallback systems for your most critical components.
Imagine your primary internet connection goes down. For most businesses, that means everything stops. But with a redundant setup, your network would automatically failover to a secondary internet line from a completely different provider. Your team might not even realize there was a problem.
This same logic applies to your internal hardware:
- Dual Routers: If the main router dies, the second one kicks in instantly.
- Failover Switches: Critical network traffic is automatically rerouted if a core switch fails.
Putting these systems in place is a serious investment, but the cost of downtime is almost always higher. To make sure your backups and redundant systems are configured correctly and always ready to go, it’s often wise to look into a structured support plan. A yearly maintenance contract can offer the expert oversight needed to ensure this ultimate insurance policy for your network never lets you down.
Bring in the Experts: How Managed Services Can Transform Your Network Security
For most businesses, trying to handle all aspects of network security internally is a losing battle. It’s like being your own lawyer, accountant, and doctor all at once—you might know a little, but you lack the deep, specialized expertise needed to do it right. The reality is that modern cyber threats require a level of skill and constant attention that most in-house teams just can’t sustain.
This is exactly why partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) is often the smartest move a business can make.

Think of an MSP as an extension of your own team. They bring the 24/7 monitoring, proactive upkeep, and immediate threat response capabilities that would be astronomically expensive to build from scratch. You get access to enterprise-level security tools and certified experts without the hefty price tag of hiring them directly. It’s an immediate and significant upgrade to your entire security framework.
Gaining a Strategic Partner, Not Just an Outsourced Vendor
Working with an MSP isn’t just about handing off IT tickets. It’s about bringing on a strategic partner who is wholly dedicated to the health and performance of your network. This simple shift allows your internal staff to stop putting out daily fires and start focusing on projects that actually move the business forward.
This approach is catching on quickly, especially in the Middle East, where company boards are finally making cyber defense a top-line priority. In fact, recent data shows that in 41% of organizations, the CISO and the board are now working together on cyber strategy, treating security as essential for business continuity. This top-down focus is crucial for building resilient networks. You can dive deeper into these regional cybersecurity budgeting trends from PwC.
An MSP shifts your IT from a reactive expense to a proactive asset. They’re not just there to fix things when they break; they work to prevent problems from ever happening, keeping your network consistently secure and reliable.
By placing your network in the hands of specialists, you get two invaluable things: peace of mind and predictable monthly costs. A good partner will handle everything from the initial network hardening to continuous support and monitoring. For businesses here, securing expert IT support in Abu Dhabi provides a clear path to achieving this level of protection, ensuring your infrastructure is solid, safe, and ready for the future.
Your Top Network Security Questions, Answered
When you’re trying to lock down your business network, a lot of questions pop up. I get it. Let’s cut through the noise and get you some straight answers to the things I hear most often from business owners.
Do I Really Need a VPN for My Team?
In a word: yes. If you have anyone on your team who ever works outside the office—whether from home, a coffee shop, or an airport—a Virtual Private Network (VPN) isn’t just a good idea, it’s essential.
A VPN creates a private, encrypted tunnel over the public internet. Think of it as a secure armored truck for your data. Without it, any sensitive company information sent over public Wi-Fi is like an open postcard, easily read by anyone snooping on the network.
Is Cloud Storage a Secure Backup Option?
Cloud storage is a fantastic and critical piece of any solid backup plan. It’s perfect for the “off-site” copy in the classic 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies, two different media, one off-site). Top-tier cloud providers use heavy-duty encryption to protect your files both as they’re being uploaded and while they’re sitting on their servers.
But here’s the key: the cloud shouldn’t be your only backup. You still need a local copy. Combining cloud storage with a physical backup on-site gives you the best of both worlds—fast local recovery if you need it, and an off-site safety net if something happens to your office.
How Often Should We Change Passwords?
This is a big one, because the old advice has changed. The days of forcing everyone to change their passwords every 90 days are over. We’ve learned that this often leads to people creating weaker, predictable passwords just to meet the requirement.
Today, the focus is squarely on two things: password complexity and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). A long, complex, unique password for each service, beefed up with an MFA prompt (like a code from your phone), is infinitely more secure than frequently changing a simple password. Enforce strong passwords and turn on MFA everywhere you possibly can.
Ready to build a network that’s not just secure, but truly reliable? The experts at OMX Solutions L.L.C. provide the strategic guidance and hands-on support your business needs. Contact us today to secure your digital foundation.
